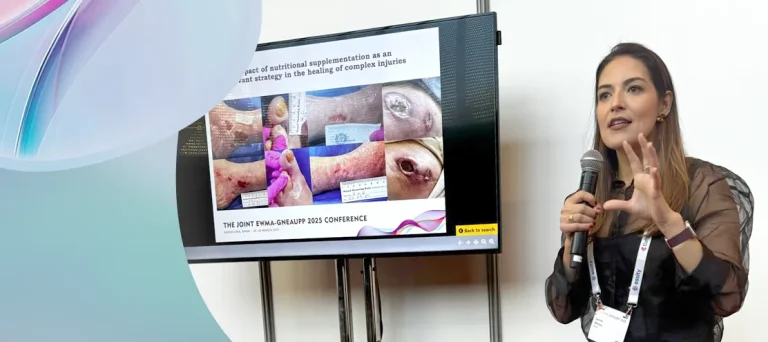
Wound healing is a process that requires adequate nutrition to occur satisfactorily1.
CORRECTMax contains the specific nutrients that support the wound healing process2-12. Nutrition plays a crucial role in each of the healing phases. Adequate supply of the nutrients involved in the healing process can contribute to faster and more efficient recovery3,4.
For the healing process to take place satisfactorily, it is important to ensure the supply of signaling nutrients such as bioactive collagen peptides and L-arginine2-7. In addition, vitamins A, C and E are needed at all stages of healing and are indispensable for cell proliferation9-11. Selenium and zinc are also fundamental minerals in these stages11.
CORRECTMax consists of*:
- 10g of bioactive collagen peptides
- 3g L-arginine
- 612 mcg of vitamin A
- 508 mg of vitamin C
- 15.2 mg vitamin E
- 30 mcg selenium and
- 15.2 mg zinc
*Values per 20g serving (2 sachets)
The supply of these specific nutrients, in the ideal quantity, could be the key to wound treatment, considering that they are often not ingested in sufficient quantities through food. Studies show that supplementing with these nutrients has been shown to reduce healing time, impacting on quality of life and costs with dressings and other necessary devices1,3,4,13,14. In addition, CORRECTMax contains isomaltulose, a slowly absorbed carbohydrate with a low glycemic index, which helps with glycemic control15, an important factor for healing. It has 64 calories in the recommended daily dose, making it an excellent strategy for those individuals who don't need a high-calorie supplement, such as the obese, diabetics and others.

References
- Allen B. Effects of a comprehensive nutritional program on pressure ulcer healing, length of hospital stay, and charges to patients. Clin Nurs Res. 2013;22(2):186-205.
- Bottoni A et al. Role of Nutrition in Healing. Revista Ciências em Saúde, 201;1(1)., Apr 2011.
- Brazilian Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (BRASPEN). Say No to Pressure Injury Campaign. BRASPEN J 2020; 35 (Suppl. 1).
- National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel and Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance. Prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers: quick reference guide. Osborne Park: Cambridge Media; 2019.
- Gould A et al. Arginine metabolism and wound healing. Wound Healing Southern Africa 2008;1(1): 48-50.
- Miyab KB et al. The effect of a hydrolyzed collagen-based supplement on wound healing in patients with burn: A randomized double-blind pilot clinical trial. Burns. 2020 Feb;46(1):156-163.
- Sugihara F et al. Ingestion of bioactive collagen hydrolysates enhanced pressure ulcer healing in a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study. Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 30;8(1):11403.
- Mistry K et al. Potentiating cutaneous wound healing in young and aged skin with nutraceutical collagen peptides. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021 Jan;46(1):109-117.
- Moores J. Vitamin C: a wound healing perspective. Br J Community Nurs. 2013 Dec;Suppl:56, S8-11.
- Polcz ME, Barbul A. The Role of Vitamin A in Wound Healing. Nutr Clin Pract. 2019 Oct;34(5):695-700.
- Thompson C, Fuhrman MP. Nutrients and wound healing: still searching for the magic bullet. Nutr Clin Pract 2005; 20(3):331-347.
- Palmieri B, Vadalà M, Laurino C. Nutrition in wound healing: investigation of the molecular mechanisms, a narrative review. J Wound Care. 2019 Oct 2;28(10):683-693.
- Waitzberg, DL. Oral, Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition in clinical practice. São Paulo: Atheneu Publishing House, 2009. 4th edition.
- Hisashige A, Ohura T. Cost-effectiveness of nutritional intervention on healing of pressure ulcers. Clin Nutr. 2012 Dec;31(6):868-74.
- Holub I et al. Novel findings on the metabolic effects of the low glycaemic carbohydrate isomaltulose (Palatinose). Brit J Nutr. 2010;103:1730-1737.