O nosso intestino conta com mais de 100 trilhões de microrganismos, que juntos compõem a flora intestinal. E para estar com a saúde em dia é preciso manter a microbiota intestinal equilibrada com o consumo regular de probióticos e prebióticos.
Você sabe o que eles são e qual é a diferença entre eles? Confira o conteúdo que preparamos para entender os benefícios de cada um deles de forma simples e descomplicada:
O que são probióticos?
Os probióticos são microrganismos vivos, as chamadas bactérias “do bem”, que quando consumidas adequadamente promovem o equilíbrio da microbiota intestinal.
Qual a diferença entre prebióticos e probióticos?
Já os prebióticos são componentes alimentares não-digeríveis derivados dos carboidratos, principalmente as fibras, que alimentam e contribuem para o desenvolvimento das bactérias benéficas, os probióticos.
Quanto mais prebióticos no organismo, mais as bactérias (probióticos) se reproduzem e garantem o bom funcionamento do intestino.
E o que faz mal para microbiota?
Fique de olho: O consumo de açúcar em excesso, gorduras saturadas, cigarro, álcool, estresse e sedentarismo são alguns dos hábitos que podem prejudicar e desequilibrar a microbiota intestinal.
O segredo está em manter uma rotina de exercícios acompanhado de uma alimentação saudável e equilibrada, sem esquecer da ingestão adequada de água.
Quais são os benefícios do consumo de probióticos?
Os probióticos, esses pequenos aliados invisíveis, desempenham papéis cruciais em nossa saúde geral. Vamos aprofundar alguns dos benefícios notáveis que essas bactérias amigáveis proporcionam:
- Redução Significativa dos Níveis de Colesterol Total com Diminuição do LDL: Os probióticos mostraram-se eficazes na promoção de um perfil lipídico saudável, contribuindo para a redução do colesterol total e do LDL.
- Melhora da Digestão de Proteínas: Ao otimizar a quebra de proteínas, os probióticos facilitam a absorção dos blocos construtores essenciais para o corpo.
- Aumento da Absorção de Vitaminas e Minerais: Facilitando a absorção de nutrientes, os probióticos garantem que seu corpo aproveite ao máximo os benefícios dos alimentos.
- Promoção da Digestão da Lactose em Indivíduos com Intolerância: Para aqueles que lutam com a intolerância à lactose, os probióticos podem oferecer alívio ao ajudar na digestão desse açúcar do leite.
- Estimulação do Sistema Imune: Reforçando as defesas naturais do corpo, os probióticos desempenham um papel crucial na promoção da saúde imunológica.
- Alívio da Constipação: Ao regular o trânsito intestinal, os probióticos podem aliviar a constipação e promover a regularidade.
- Efeitos Anti-hipertensivos: Alguns probióticos demonstraram ter efeitos benéficos na redução da pressão arterial.
- Redução da Atividade Ulcerativa de Helicobacter pylori: Combatendo as bactérias prejudiciais, os probióticos podem ajudar a reduzir a atividade ulcerativa associada ao Helicobacter pylori.
- Controle da Colite Induzida por Rotavírus e por Clostridium difficile: Os probióticos mostraram potencial em controlar condições inflamatórias intestinais.
- Prevenção de Infecções Urogenitais: Mantendo o equilíbrio da flora, os probióticos podem ajudar na prevenção de infecções no trato urogenital.
- Redução do Risco de Câncer de Cólon: Estudos sugerem que o consumo regular de probióticos pode estar associado a um menor risco de câncer de cólon.
Essas são apenas algumas razões pelas quais incorporar probióticos em sua rotina pode ser uma escolha sábia para a saúde a longo prazo. Consulte sempre um profissional de saúde para orientação personalizada.
Qual a importância para o paciente com câncer?
Para aqueles que enfrentam a batalha contra o câncer, cada elemento de suporte à saúde é crucial. Os probióticos emergem como aliados valiosos nesse contexto desafiador, oferecendo benefícios específicos que podem impactar positivamente a jornada do paciente. Vamos explorar a importância desses microrganismos:
- Fortalecimento do Sistema Imunológico: Pacientes em tratamento muitas vezes experimentam uma supressão do sistema imunológico. Os probióticos, ao fortalecerem as defesas naturais do corpo, desempenham um papel fundamental na resistência a infecções e na promoção da recuperação.
- Alívio de Efeitos Colaterais: Terapias contra o câncer frequentemente causam efeitos colaterais gastrointestinais, como náuseas, diarreia e constipação. Probióticos podem ajudar a aliviar esses sintomas, melhorando a saúde intestinal.
- Suporte à Saúde Digestiva: As terapias oncológicas podem afetar negativamente o equilíbrio da flora intestinal. Probióticos auxiliam na restauração desse equilíbrio, melhorando a digestão e absorção de nutrientes essenciais.
- Redução da Inflamação: Certos probióticos demonstraram propriedades anti-inflamatórias, o que pode ser benéfico para pacientes com câncer, visto que a inflamação crônica pode contribuir para o desenvolvimento e progressão da doença.
- Manutenção do Peso e Nutrição Adequada: A manutenção do peso e a garantia de uma nutrição adequada são desafios comuns durante o tratamento do câncer. Probióticos podem desempenhar um papel na absorção eficiente de nutrientes e na regulação do peso corporal.
- Equilíbrio Psicossocial: A saúde mental é uma parte integral do tratamento do câncer. Alguns estudos sugerem que a microbiota intestinal pode influenciar o equilíbrio emocional. Nesse sentido, os probióticos podem ter um papel indireto, mas significativo, na saúde mental dos pacientes.
É imperativo ressaltar que a inclusão de probióticos no plano de cuidados deve ser discutida com a equipe médica, considerando as circunstâncias únicas de cada paciente. Essas bactérias oferecem um apoio valioso, mas sua implementação deve ser cuidadosamente personalizada para garantir benefícios máximos e segurança.
Quais são os benefícios do consumo de prebióticos?
Os prebióticos, embora muitas vezes na sombra de seus primos probióticos, desempenham um papel crucial na promoção da saúde intestinal e, por extensão, na saúde geral do organismo. Vamos explorar os diversos benefícios desses compostos:
- Estímulo ao Crescimento de Bactérias Benéficas: Os prebióticos são, essencialmente, fibras não digeríveis que servem como alimento para as bactérias boas no intestino. Ao fazer isso, promovem o crescimento e a atividade de bactérias probióticas, essenciais para a saúde digestiva.
- Melhoria da Saúde Intestinal: Ao alimentar seletivamente as bactérias benéficas, os prebióticos contribuem para a manutenção de um ambiente intestinal saudável. Isso é crucial para prevenir condições como a síndrome do intestino irritável e outras doenças gastrointestinais.
- Reforço do Sistema Imunológico: Uma parte significativa do sistema imunológico reside no trato gastrointestinal. Ao promover um ambiente intestinal saudável, os probióticos auxiliam na ativação e fortalecimento das defesas naturais do organismo.
- Controle do Peso: Alguns prebióticos têm sido associados à regulação do apetite e do peso corporal. Ao influenciar a microbiota intestinal, podem afetar positivamente os processos metabólicos relacionados ao peso.
- Gestão da Glicose: Estudos indicam que os prebióticos podem influenciar a absorção de glicose no intestino, contribuindo para a estabilidade dos níveis de açúcar no sangue. Isso é especialmente relevante para pessoas com diabetes ou em risco de desenvolver a condição.
- Promoção da Saúde Cardiovascular: A fermentação dos prebióticos no cólon pode resultar na produção de substâncias benéficas, como ácidos graxos de cadeia curta. Esses ácidos têm sido associados à redução dos níveis de colesterol e à promoção da saúde cardiovascular.
- Benefícios Cognitivos: Embora em estágios iniciais de pesquisa, alguns estudos sugerem que a saúde intestinal influencia a saúde cerebral. Os prebióticos podem, indiretamente, contribuir para a saúde cognitiva.
É fundamental destacar que a diversidade na dieta desempenha um papel crucial na promoção de uma microbiota intestinal saudável.
Quais são os alimentos prebióticos e probióticos?
Ao combinar alimentos probióticos e prebióticos, você cria um ambiente sinérgico que favorece o crescimento e a atividade das bactérias benéficas no seu intestino. Esta dança harmoniosa entre microrganismos e fibras contribui significativamente para a saúde digestiva e o bem-estar geral. Aproveite esses alimentos como parte de uma dieta equilibrada para nutrir seu intestino e fortalecer sua saúde:
Probióticos
Os probióticos são microrganismos vivos que, quando consumidos em quantidades adequadas, conferem benefícios à saúde do hospedeiro. Eles são encontrados em alimentos fermentados e, quando integrados à dieta regularmente, podem promover um equilíbrio saudável da microbiota intestinal. Alguns dos alimentos ricos em probióticos incluem:
- Iogurte: Uma fonte popular de bactérias probióticas, o iogurte não apenas é delicioso, mas também oferece benefícios digestivos.
- Kefir: Uma bebida fermentada que contém uma mistura única de bactérias e leveduras benéficas.
- Chucrute: Repolho fermentado que não apenas adiciona um toque saboroso aos pratos, mas também fornece uma dose saudável de probióticos.
- Kimchi: Uma iguaria coreana feita de vegetais fermentados, principalmente repolho e rabanete, rica em bactérias boas.
- Missô: Uma pasta fermentada à base de soja, amplamente utilizada na culinária japonesa.
- Picles: Vegetais em conserva podem ser uma fonte saborosa e crocante de probióticos.
Prebióticos
Os prebióticos são fibras não digeríveis que servem como alimento para as bactérias benéficas no intestino, ajudando-as a prosperar. Incluir alimentos ricos em probióticos na dieta é fundamental para promover um ambiente intestinal saudável. Algumas opções deliciosas incluem:
- Alho: Além de adicionar sabor às refeições, o alho contém prebióticos que alimentam as bactérias boas no intestino.
- Cebola: Rica em fibras prebióticas, a cebola é versátil e pode ser incorporada em várias receitas.
- Banana: Uma fonte natural de fruto-oligossacarídeos (FOS), uma forma de prebiótico.
- Aspargos: Esses vegetais verdes fornecem uma boa dose de inulina, outra fibra prebiótica.
- Alcachofra: Uma excelente fonte de inulina, que estimula o crescimento de bactérias benéficas.
- Cevada: Este grão integral contém beta-glucanos, uma forma de fibra prebiótica.
O que são alimentos simbióticos?
Os alimentos simbióticos são verdadeiros maestros na sinfonia da saúde digestiva, combinando elementos probióticos e prebióticos para criar uma experiência verdadeiramente harmoniosa para o seu intestino.
Este é um exemplo perfeito de cooperação na natureza, onde as bactérias probióticas se alimentam das fibras prebióticas, fortalecendo sua presença e atividade no intestino.
Exemplos de Alimentos Simbióticos:
- Iogurte com Inulina: Um clássico exemplo, onde a inulina (prebiótico) é adicionada ao iogurte, criando um ambiente propício para as bactérias probióticas.
- Kefir com Fruto-oligossacarídeos (FOS): Uma deliciosa combinação, onde o kefir fornece probióticos, enquanto os FOS oferecem o sustento necessário.
- Kimchi com Alho: A fermentação do kimchi traz probióticos, enquanto o alho contribui com seus prebióticos.
Benefícios dos Alimentos Simbióticos:
- Equilíbrio da Microbiota: A combinação de probióticos e prebióticos promove um ambiente intestinal saudável.
- Melhoria da Digestão: Contribuem para uma digestão mais eficiente, otimizando a absorção de nutrientes.
- Refúgio contra Patógenos: Reforçam as defesas intestinais, dificultando a colonização por bactérias nocivas.
Cuide do seu intestino com esta sinfonia de benefícios e desfrute de uma saúde digestiva vibrante e resiliente.
Conclusão
Ao entender a diferença entre probióticos, os benéficos “super-heróis” microscópicos, e prebióticos, os “nutrientes” que os alimentam, abrimos as portas para uma abordagem holística da saúde digestiva.
Os benefícios são vastos e abrangem desde a redução dos níveis de colesterol até o fortalecimento do sistema imune. A jornada continua, pois a ciência nutricional é um campo sempre em evolução, repleto de descobertas fascinantes.

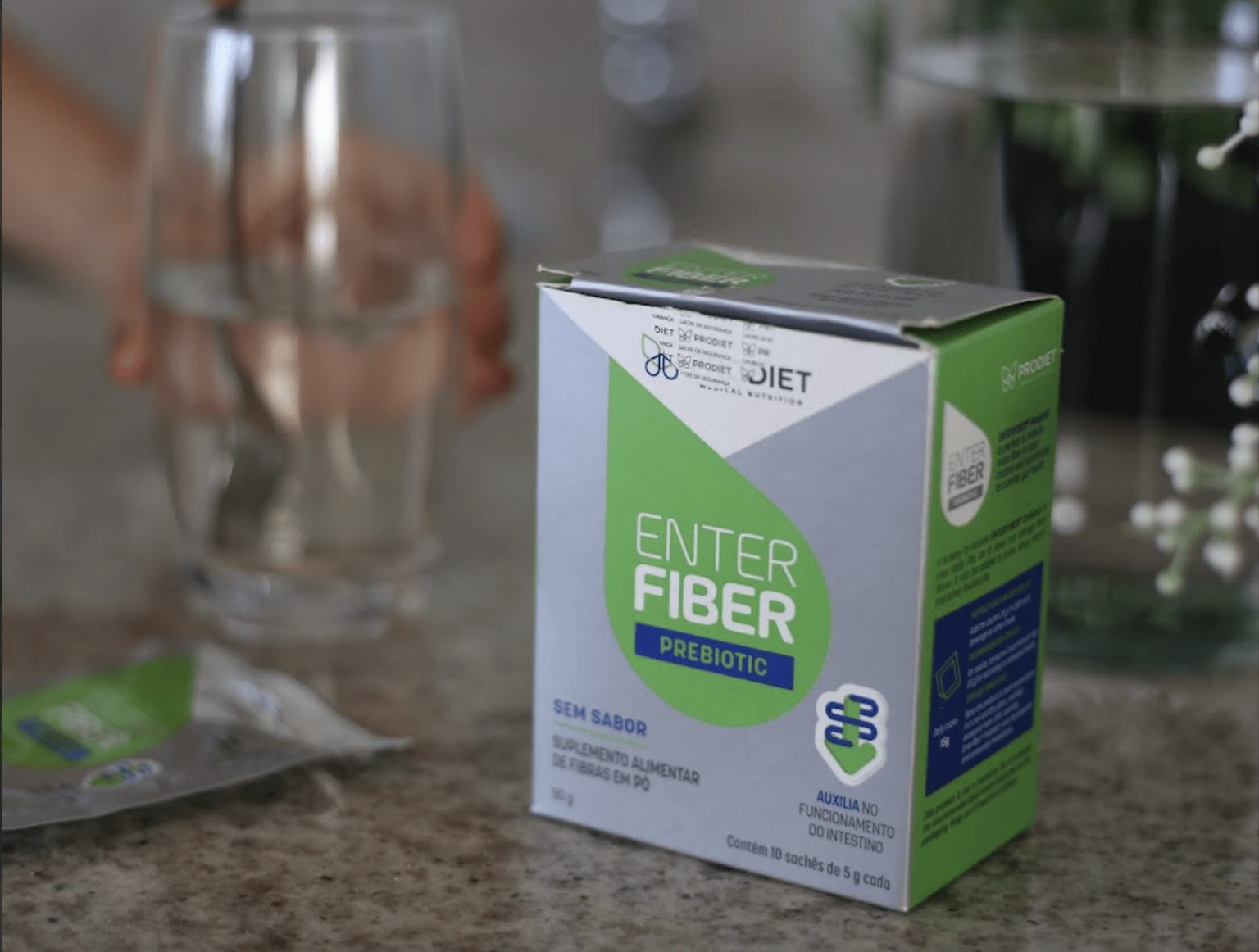
O EnterFiber Prebiotic conta com fibras prebióticas, polidextrose e frutooligossacarídeos (FOS), que enriquecem a dieta e promovem o equilíbrio da flora intestinal, além de contribuir com a imunidade.
O sachê é muito prático, pode ser levado na bolsa para te acompanhar diariamente e pode ser adicionado a sucos, água, iogurtes, sem adição de sabor.
Encontre o distribuidor mais perto de você.
Gostou das dicas? Siga-nos nas redes Instagram, Facebook e LinkedIn e acompanhe as nossas novidades.